Our talented team know how to excite, inspire and engage. With backgrounds in events, entertainment and travel, we’re full of ideas for amazing prizes and unforgettable incentives!
At Fulcrum, we all come to work every day because we have a shared love of travel and delivering once-in-a-lifetime experiences.
Our team meetings are buzzing with fresh ideas, brand new experiences and glowing feedback from our travellers. We know what makes a great incentive, we have an encyclopaedic knowledge of the best experiences around the world, and we have an ever-expanding ‘little black book’ of the most exclusive suppliers in the business.
In addition to our creative ideas and experience, we know that our clients value our expertise and dedication to solving problems rather than creating them. Prizes and incentives are our world, but we understand that our clients have other priorities, so we make sure we’re delivering our ideas on-time, on-budget and on-brand. We thrive on tight deadlines, logistical challenges and creating perfectly tailored solutions, without the headaches!
About us
Perfect solutions every time
As a leading marketing Agency, we’re immensely proud to work with brands and agencies across a huge range of sectors and industries, giving us an unrivalled breadth of experience.
we have created and fulfilled prizes for promotions and activations across the world.
Our aim: help our clients achieve their goals through our experience and expertise, taking the stress and hassle out of prize fulfilment.
We work for both direct brands and agencies, often in collaboration or with other specialist agencies and partners. Many of our clients have existing assets – from festival tickets to sports hospitality – which we help them to build into the best possible prize packages. Others want to create unique, eye-catching marketing and btl content around their prize winners. We can deal with winners from any country and in any language; we can provide a full btl management service; we can even source camera crews for content capture.
Whatever your brief, we’ve got it covered.
SALES INCENTIVES
Driving sales and performance through tailored, flexible incentive programmes
With pressure always on to drive sales and performance, sales incentives are an essential part of rewarding achievement within many companies. From internal staff reward programmes to dealer and channel incentives, there’s no better way to create a happy, engaged and motivated workforce.
Our main goal is to understand your people and what makes them tick. From hundreds in a call centre team to a small on ground sales team, a clear overview of your audience is the most important part of the process. By taking a best approach, offering maximum choice and flexibility, we create incentives which are targeted, effective and tailored to your team.
Whether it’s sales rewards, dealer incentives or channel incentives, drop us a line; we’d love to help you drive sales with our fresh and creative approach to prizes and incentives. From once-in-a-lifetime holidays to mini-breaks, high-street vouchers and designer goods, you can rest assured that with Fulcrum you’re in safe hands.
24 hour turnaround for urgent briefs
Topline ideas within 2 hours if needed
Competitive fixed quotes with no hidden costs
Expert Winner Management and Fulfilment
Retail Marketing organizations | Interactive marketing Plan Warje
Components of the Strategic Planning Process
2.2 Components of the Strategic Planning Process
Learning Objectives
- Explain how a mission statement helps a company with its strategic planning.
- Describe how a firm analyzes its internal environment.
- Describe the external environment a firm may face and how it is analyzed.
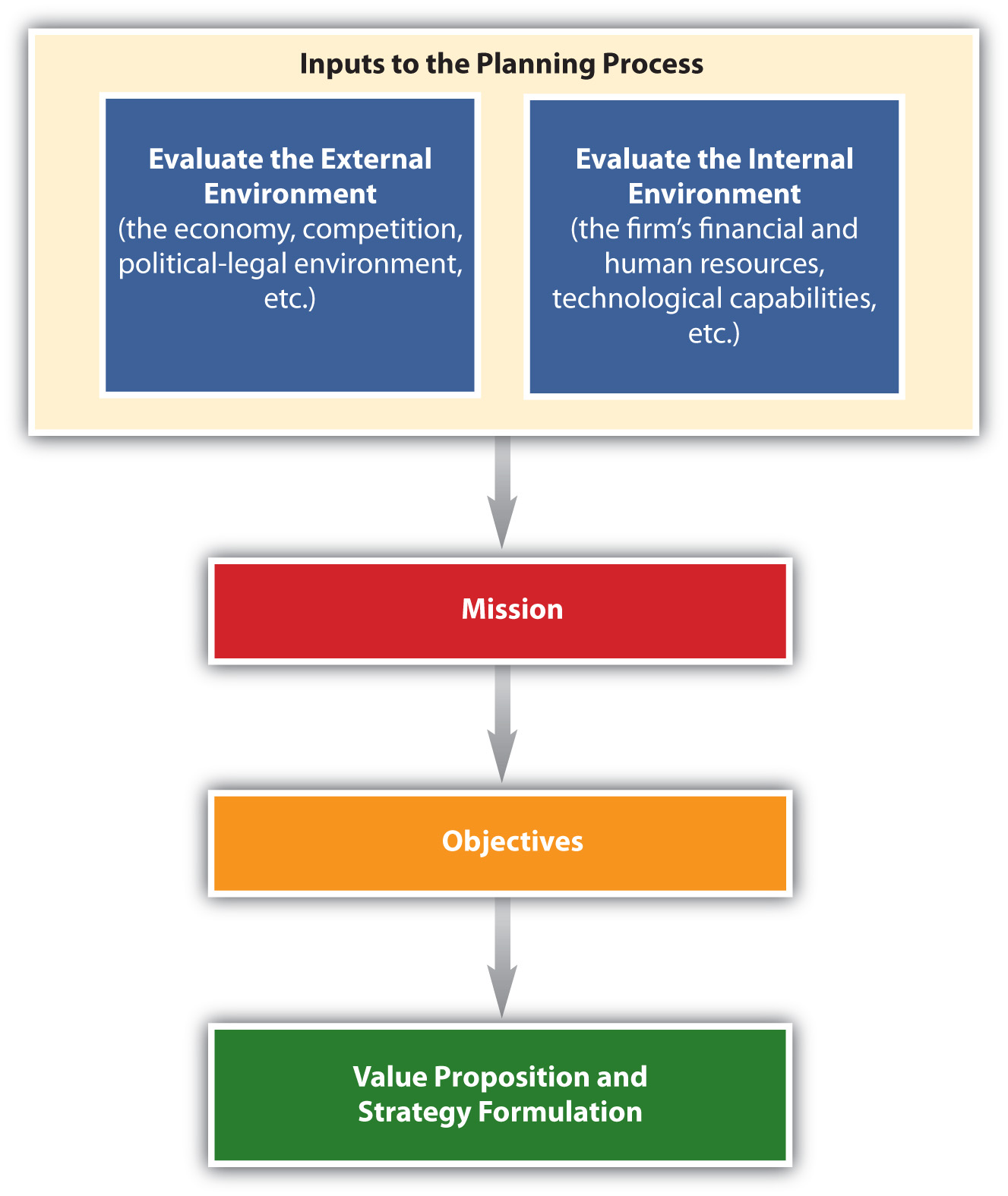
Strategic planning is a process that helps an organization allocate its resources to capitalize on opportunities in the marketplace. Typically, it is a long-term process. The strategic planning process includes conducting a situation analysis and developing the organization’s mission statement, objectives, value proposition, and strategies. Figure 2.2 “The Strategic Planning Process” shows the components of the strategic planning process. Let’s now look at each of these components.
Conducting a Situation Analysis
As part of the strategic planning process, a situation analysis must be conducted before a company can decide on specific actions. A situation analysis involves analyzing both the external (macro and micro factors outside the organization) and the internal (company) environments. Figure 2.2 “The Strategic Planning Process” and Figure 2.3 “Elements of a SWOT Analysis” show examples of internal and external factors and in a SWOT analysis. The firm’s internal environment—such as its financial resources, technological resources, and the capabilities of its personnel and their performance—has to be examined. It is also critical to examine the external macro and micro environments the firm faces, such as the economy and its competitors. The external environment significantly affects the decisions a firm makes, and thus must be continuously evaluated. For example, during the economic downturn in 2008–2009, businesses found that many competitors cut the prices of their products drastically. Other companies reduced package sizes or the amount of product in packages. Firms also offered customers incentives (free shipping, free gift cards with purchase, rebates, etc.) to purchase their goods and services online, which allowed businesses to cut back on the personnel needed to staff their brick-and-mortar stores. While a business cannot control things such as the economy, changes in demographic trends, or what competitors do, it must decide what actions to take to remain competitive—actions that depend in part on their internal environment.
Conducting a SWOT Analysis
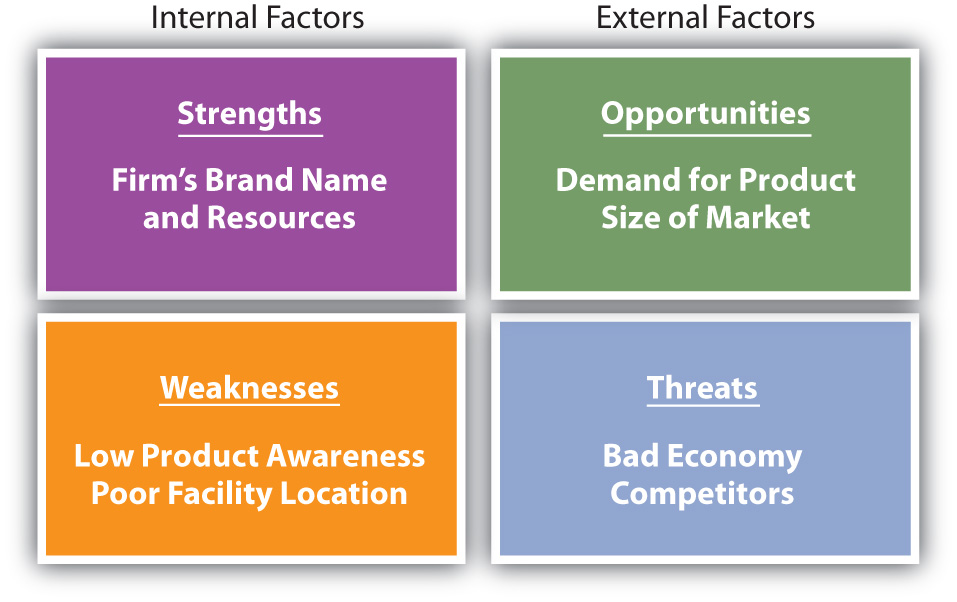
Based on the situation analysis, organizations analyze their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, or conduct what’s called a SWOT analysis. Strengths and weaknesses are internal factors and are somewhat controllable. For example, an organization’s strengths might include its brand name, efficient distribution network, reputation for great service, and strong financial position. A firm’s weaknesses might include lack of awareness of its products in the marketplace, a lack of human resources talent, and a poor location. Opportunities and threats are factors that are external to the firm and largely uncontrollable. Opportunities might entail the international demand for the type of products the firm makes, few competitors, and favorable social trends such as people living longer. Threats might include a bad economy, high interest rates that increase a firm’s borrowing costs, and an aging population that makes it hard for the business to find workers.
You can conduct a SWOT analysis of yourself to help determine your competitive advantage. Perhaps your strengths include strong leadership abilities and communication skills, whereas your weaknesses include a lack of organization. Opportunities for you might exist in specific careers and industries; however, the economy and other people competing for the same position might be threats. Moreover, a factor that is a strength for one person (say, strong accounting skills) might be a weakness for another person (poor accounting skills). The same is true for businesses. See Figure 2.3 “Elements of a SWOT Analysis” for an illustration of some of the factors examined in a SWOT analysis.
The easiest way to determine if a factor is external or internal is to take away the company, organization, or individual and see if the factor still exists. Internal factors such as strengths and weaknesses are specific to a company or individual, whereas external factors such as opportunities and threats affect multiple individuals and organizations in the marketplace. For example, if you are doing a situation analysis on PepsiCo and are looking at the weak economy, take PepsiCo out of the picture and see what factors remain. If the factor—the weak economy—is still there, it is an external factor. Even if PepsiCo hadn’t been around in 2008–2009, the weak economy reduced consumer spending and affected a lot of companies.
Assessing the Internal Environment
As we have indicated, when an organization evaluates which factors are its strengths and weaknesses, it is assessing its internal environment. Once companies determine their strengths, they can use those strengths to capitalize on opportunities and develop their competitive advantage. For example, strengths for PepsiCo are what are called “mega” brands, or brands that individually generate over $1 billion in sales1. These brands are also designed to contribute to PepsiCo’s environmental and social responsibilities.
PepsiCo’s brand awareness, profitability, and strong presence in global markets are also strengths. Especially in foreign markets, the loyalty of a firm’s employees can be a major strength, which can provide it with a competitive advantage. Loyal and knowledgeable employees are easier to train and tend to develop better relationships with customers. This helps organizations pursue more opportunities.
Although the brand awareness for PepsiCo’s products is strong, smaller companies often struggle with weaknesses such as low brand awareness, low financial reserves, and poor locations. When organizations assess their internal environments, they must look at factors such as performance and costs as well as brand awareness and location. Managers need to examine both the past and current strategies of their firms and determine what strategies succeeded and which ones failed. This helps a company plan its future actions and improves the odds they will be successful. For example, a company might look at packaging that worked very well for a product and use the same type of packaging for new products. Firms may also look at customers’ reactions to changes in products, including packaging, to see what works and doesn’t work. When PepsiCo changed the packaging of major brands in 2008, customers had mixed responses. Tropicana switched from the familiar orange with the straw in it to a new package and customers did not like it. As a result, Tropicana changed back to their familiar orange with a straw after spending $35 million for the new package design.
Video Clip
Tropicana’s Recent Ad
Tropicana’s recent ad left out the familiar orange with a straw.
Individuals are also wise to look at the strategies they have tried in the past to see which ones failed and which ones succeeded. Have you ever done poorly on an exam? Was it the instructor’s fault, the strategy you used to study, or did you decide not to study? See which strategies work best for you and perhaps try the same type of strategies for future exams. If a strategy did not work, see what went wrong and change it. Doing so is similar to what organizations do when they analyze their internal environments.
Assessing the External Environment
Analyzing the external environment involves tracking conditions in the macro and micro marketplace that, although largely uncontrollable, affect the way an organization does business. The macro environment includes economic factors, demographic trends, cultural and social trends, political and legal regulations, technological changes, and the price and availability of natural resources. Each factor in the macro environment is discussed separately in the next section. The micro environment includes competition, suppliers, marketing intermediaries (retailers, wholesalers), the public, the company, and customers. We focus on competition in our discussion of the external environment in the chapter. Customers, including the public will be the focus of Chapter 3 “Consumer Behavior: How People Make Buying Decisions” and marketing intermediaries and suppliers will be discussed in Chapter 8 “Using Marketing Channels to Create Value for Customers” and Chapter 9 “Using Supply Chains to Create Value for Customers”.
When firms globalize, analyzing the environment becomes more complex because they must examine the external environment in each country in which they do business. Regulations, competitors, technological development, and the economy may be different in each country and will affect how firms do business. To see how factors in the external environment such as technology may change education and lives of people around the world, watch the videos “Did You Know 2.0?” and “Did You Know 3.0?” which provide information on social media sites compared to populations in the world. Originally created in 2006 and revised in 2007, the video has been updated and translated into other languages. Another edition of “Did You Know?” (4.0) focused on changing media and technology and showed how information may change the world as well as the way people communicate and conduct business.
Video Clip
Did You Know 2.0?
To see how the external environment and world are changing and in turn affecting marketing strategies, check out “Did You Know 2.0?”
Video Clip
Did You Know 4.0?
To see how fast things change and the impact of technology and social media, visit “Did You Know 4.0?”
Although the external environment affects all organizations, companies must focus on factors that are relevant for their operations. For example, government regulations on food packaging will affect PepsiCo but not Goodyear. Similarly, students getting a business degree don’t need to focus on job opportunities for registered nurses.
The Competitive Environment
All organizations must consider their competition, whether it is direct or indirect competition vying for the consumer’s dollar. Both nonprofit and for-profit organizations compete for customers’ resources. Coke and Pepsi are direct competitors in the soft drink industry, Hilton and Sheraton are competitors in the hospitality industry, and organizations such as United Way and the American Cancer Society compete for resources in the nonprofit sector. However, hotels must also consider other options that people have when selecting a place to stay, such as hostels, dorms, bed and breakfasts, or rental homes.
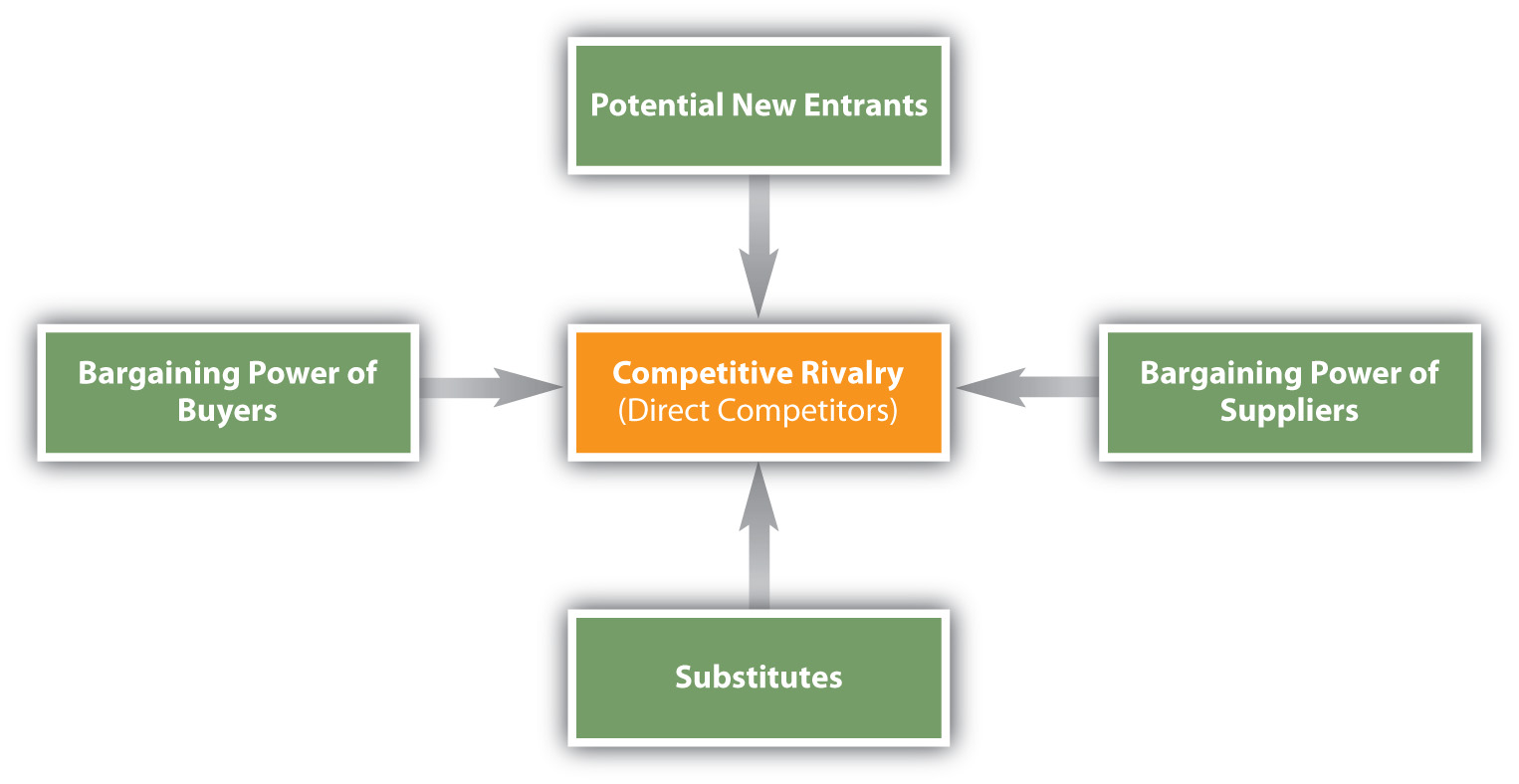
A group of competitors that provide similar products or services form an industry. Michael Porter, a professor at Harvard University and a leading authority on competitive strategy, developed an approach for analyzing industries. Called the five forces model (Porter, 1980) and shown in Figure 2.5 “Five Forces Model”, the framework helps organizations understand their current competitors as well as organizations that could become competitors in the future. As such, firms can find the best way to defend their position in the industry.
Competitive Analysis
When a firm conducts a competitive analysis, they tend to focus on direct competitors and try to determine a firm’s strengths and weaknesses, its image, and its resources. Doing so helps the firm figure out how much money a competitor may be able to spend on things such as research, new product development, promotion, and new locations. Competitive analysis involves looking at any information (annual reports, financial statements, news stories, observation details obtained on visits, etc.) available on competitors. Another means of collecting competitive information utilizes mystery shoppers, or people who act like customers. Mystery shoppers might visit competitors to learn about their customer service and their products. Imagine going to a competitor’s restaurant and studying the menu and the prices and watching customers to see what items are popular and then changing your menu to better compete. Competitors battle for the customer’s dollar and they must know what other firms are doing. Individuals and teams also compete for jobs, titles, and prizes and must figure out the competitors’ weaknesses and plans in order to take advantage of their strengths and have a better chance of winning.
According to Porter, in addition to their direct competitors (competitive rivals), organizations must consider the strength and impact the following could have (Porter, 1980):
- Substitute products
- Potential entrants (new competitors) in the marketplace
- The bargaining power of suppliers
- The bargaining power of buyers
When any of these factors change, companies may have to respond by changing their strategies. For example, because buyers are consuming fewer soft drinks these days, companies such as Coke and Pepsi have had to develop new, substitute offerings such as vitamin water and sports drinks. However, other companies such as Dannon or Nestlé may also be potential entrants in the flavored water market. When you select a hamburger fast-food chain, you also had the option of substitutes such as getting food at the grocery or going to a pizza place. When computers entered the market, they were a substitute for typewriters. Most students may not have ever used a typewriter, but some consumers still use typewriters for forms and letters.
Figure 2.6
When personal computers were first invented, they were a serious threat to typewriter makers such as Smith Corona.
mpclemens – Smith-Corona Classic 12 – CC BY 2.0.
Suppliers, the companies that supply ingredients as well as packaging materials to other companies, must also be considered. If a company cannot get the supplies it needs, it’s in trouble. Also, sometimes suppliers see how lucrative their customers’ markets are and decide to enter them. Buyers, who are the focus of marketing and strategic plans, must also be considered because they have bargaining power and must be satisfied. If a buyer is large enough, and doesn’t purchase a product or service, it can affect a selling company’s performance. Walmart, for instance, is a buyer with a great deal of bargaining power. Firms that do business with Walmart must be prepared to make concessions to them if they want their products on the company’s store shelves.
Lastly, the world is becoming “smaller” and a more of a global marketplace. Companies everywhere are finding that no matter what they make, numerous firms around the world are producing the same “widget” or a similar offering (substitute) and are eager to compete with them. Employees are in the same position. The Internet has made it easier than ever for customers to find products and services and for workers to find the best jobs available, even if they are abroad. Companies are also acquiring foreign firms. These factors all have an effect on the strategic decisions companies make.
The Political and Legal Environment
All organizations must comply with government regulations and understand the political and legal environments in which they do business. Different government agencies enforce the numerous regulations that have been established to protect both consumers and businesses. For example, the Sherman Act (1890) prohibits U.S. firms from restraining trade by creating monopolies and cartels. The regulations related to the act are enforced by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), which also regulates deceptive advertising. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates the labeling of consumable products, such as food and medicine. One organization that has been extremely busy is the Consumer Product Safety Commission, the group that sets safety standards for consumer products. Unsafe baby formula and toys with lead paint caused a big scare among consumers in 2008 and 2009.
Figure 2.7
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration prohibits companies from using unacceptable levels of lead in toys and other household objects, such as utensils and furniture. Mattel voluntarily recalled Sarge cars made in mid-2000.
U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission – public domain.
As we have explained, when organizations conduct business in multiple markets, they must understand that regulations vary across countries and across states. Many states and countries have different laws that affect strategy. For example, suppose you are opening up a new factory because you cannot keep up with the demand for your products. If you are considering opening the factory in France (perhaps because the demand in Europe for your product is strong), you need to know that it is illegal for employees in that country to work more than thirty-five hours per week.
The Economic Environment
The economy has a major impact on spending by both consumers and businesses, which, in turn, affects the goals and strategies of organizations. Economic factors include variables such as inflation, unemployment, interest rates, and whether the economy is in a growth period or a recession. Inflation occurs when the cost of living continues to rise, eroding the purchasing power of money. When this happens, you and other consumers and businesses need more money to purchase goods and services. Interest rates often rise when inflation rises. Recessions can also occur when inflation rises because higher prices sometimes cause low or negative growth in the economy.
During a recessionary period, it is possible for both high-end and low-end products to sell well. Consumers who can afford luxury goods may continue to buy them, while consumers with lower incomes tend to become more value conscious. Other goods and services, such as products sold in traditional department stores, may suffer. In the face of a severe economic downturn, even the sales of luxury goods can suffer. The economic downturn that began in 2008 affected consumers and businesses at all levels worldwide. Consumers reduced their spending, holiday sales dropped, financial institutions went bankrupt, the mortgage industry collapsed, and the “Big Three” U.S. auto manufacturers (Ford, Chrysler, and General Motors) asked for emergency loans.
The demographic and social and cultural environments—including social trends, such as people’s attitudes toward fitness and nutrition; demographic characteristics, such as people’s age, income, marital status, education, and occupation; and culture, which relates to people’s beliefs and values—are constantly changing in the global marketplace. Fitness, nutrition, and health trends affect the product offerings of many firms. For example, PepsiCo produces vitamin water and sports drinks. More women are working, which has led to a rise in the demand for services such as house cleaning and daycare. U.S. baby boomers are reaching retirement age, sending their children to college, and trying to care of their elderly parents all at the same time. Firms are responding to the time constraints their buyers face by creating products that are more convenient, such as frozen meals and nutritious snacks.
The composition of the population is also constantly changing. Hispanics are the fastest-growing minority in the United States. Consumers in this group and other diverse groups prefer different types of products and brands. In many cities, stores cater specifically to Hispanic customers.
Technology
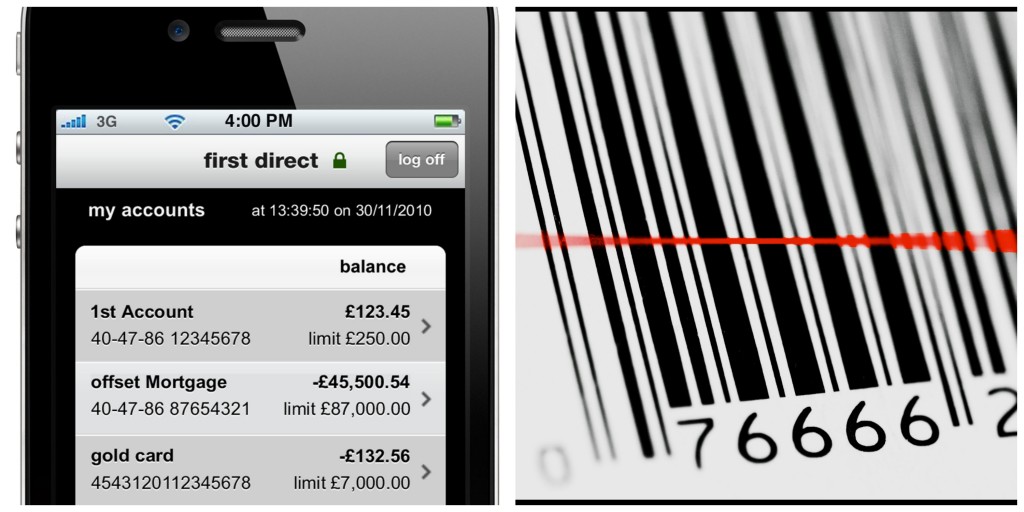
The technology available in the world is changing the way people communicate and the way firms do business. Everyone is affected by technological changes. Self-scanners and video displays at stores, ATMs, the Internet, and mobile phones are a few examples of how technology is affecting businesses and consumers. Many consumers get information, read the news, use text messaging, and shop online. As a result, marketers have begun allocating more of their promotion budgets to online ads and mobile marketing and not just to traditional print media such as newspapers and magazines. Applications for telephones and electronic devices are changing the way people obtain information and shop, allowing customers to comparison shop without having to visit multiple stores. As you saw in “Did You Know 4.0?” technology and social media are changing people’s lives. Many young people may rely more on electronic books, magazines, and newspapers and depend on mobile devices for most of their information needs. Organizations must adapt to new technologies in order to succeed.
Figure 2.9
Technology changes the way we do business. Banking on a cell phone adds convenience for customers. Bar codes on merchandise speed the checkout process.
first direct – first direct Banking ‘on the go’ iPhone App – front – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0; Paul Domenick – Lasered – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Natural Resources
Natural resources are scarce commodities, and consumers are becoming increasingly aware of this fact. Today, many firms are doing more to engage in “sustainable” practices that help protect the environment and conserve natural resources. Green marketing involves marketing environmentally safe products and services in a way that is good for the environment. Water shortages often occur in the summer months, so many restaurants now only serve patrons water upon request. Hotels voluntarily conserve water by not washing guests’ sheets and towels every day unless they request it. Reusing packages (refillable containers) and reducing the amount of packaging, paper, energy, and water in the production of goods and services are becoming key considerations for many organizations, whether they sell their prod
Door To Door Marketing
Retail Marketing organizations, Interactive marketing Plan, Corporate Marketing Solutions ,
housing society Marketing Program, Store marketing organizations, home to home marketing Supplier,
engagement marketing Supplier , onground marketing Supplier, IT Parks Marketing Supplier ,
Restaurant Marketing Supplier , college Marketing Supplier ,
B to C marketing Supplier , f to f marketing Supplier
housing society Marketing Program | Store marketing organizations Warje
We inspire the people who power your business.
No matter who you are and what you sell, the success of your business relies on your ability to engage with two critically important groups – the people who buy from you and the people who work for you. At Fulcrum, we create truly personalised incentive programmes that have the power to energize your business. Each Fulcrum initiative is designed around the specific interests and aspirations of your customers and your people. We engage and inspire the people that matter – the people who power your business.
Our Values
Client- centricity and the provision of quality service are key values. Providing a developmental and supportive marketing environment for our staff and recognising the importance of our suppliers are integral to our business ethic. Openness, honesty, transparency and a commitment to our community underpin everything we do.
Our Team
The heart and soul of what has made us so successful is our staff. It is their passion, commitment to quality and positive, can-do attitude that delivers outstanding performance to our clients and reinforces our reputation for service excellence.
From selection & recruitment through to training & development, we continually invest in our staff to ensure we have the right people, with the right skills to make sure that the job gets done right, first time.
Quality
Fulcrum has always aimed to be quality leaders in our industry. An impressive array of accreditations, for Quality, Environment, Security and Staff development are simply the kite-marks that demonstrate our core values in this respect.
Fulcrum Agencies
Over the years we have worked with agencies of all sizes and styles. We understand the hectic world of marketing and advertising and we have developed services specifically designed to adapt to short lead-times, changing needs, last minute requests and the occasional ‘sprint finish’.
Retail
With a long-history of providing services to retailers, whether major chains or small specialist outlets, it was a very easy step for us to adapt that to the on-line world. These days we can handle high-volume fulfilment for direct-to consumer on-line web-orders as we can easily provide retail replenishment and store refurbishment.
Grow a Product-Based Brand
Door To Door Marketing , Retail Marketing organizations , Interactive marketing Plan , Corporate Marketing Solutions,
housing society Marketing Program , Store marketing organizations , home to home marketing Supplier , engagement marketing Supplier , onground marketing Supplier , IT Parks Marketing Supplier , college Marketing Supplier , B to C marketing Supplier , f to f marketing Supplier
home to home marketing Supplier | Retail Marketing organizations in pune
Fulcrum Marketing Services in Pune are the catalyst to bringing your advertising vision to life. While many ideas start in a boardroom, you need experienced marketers on the ground who are able to conceptualize, plan and execute a well thought-out marketing campaign in the field.
we supply the experience, connections, relationships, and knowledge needed to maximize the potential return on investment for each of our clients as well as help identify and pursue select market opportunities as they come available, home to home marketing Supplier | Retail Marketing organizations in pune. Our local insight allows us to create exceptional investment potential for our partners and clients and enhanced living experience for our residents.
CREATING COMMUNITIES WHERE PEOPLE ARE EAGER TO LIVE AND RELUCTANT TO LEAVE
We define and position apartment homes for success. We are passionate about the residential experience and the qualitative and quantitative points that drive us to make strategic decisions that inform what a home should be — specific to its marketplace.
Results are realized through both the speed of lease-ups and financial performance of the on-going stabilized investment.
MARKET RESEARCH
We crunch the numbers, ask the questions, assess current trends and forecast future trends with detailed, up-to-date research to understand our markets; Ensuring our clients have the right data points to make the best decisions going forward.
MARKET POSITIONING
What’s the experience living here? What’s the story and name of this place? Our experience and insight allows us to identify and position each project’s distinctive offerings as its market niche. We provide an understanding that goes deeper than looking at trends. We create sought-after, thoughtfully executed apartment communities that are compatible with their surrounding neighborhoods.
| MARKETING STRATEGY Overall success relies on a thoughtful marketing strategy. In a constantly changing environment, we develop and implement each marketing initiative specific to your audience and budget. Reaching consumers in a way that educates and informs; ultimately creating product desirability and excellent rates of return. |
![]()
4 Keys to Small Business Success: Dream, Plan, Pray and Hard Work
home to home marketing Supplier | Retail Marketing organizations in pune
Retail Marketing organizations, Door To Door Marketing, Interactive marketing Plan, Corporate Marketing Solutions, housing society Marketing Program, Store marketing organizations, home to home marketing Supplier, engagement marketing Supplier, onground marketing Supplier, IT Parks Marketing Supplier, Restaurant Marketing Supplier, college Marketing Supplier , B to C marketing Supplier , f to f marketing Supplier, pune , mumbai
marketing Team in Agripada
ABOUT FIELD MARKETING
WHAT IS FIELD MARKETING? Field marketing and marketing Team in Agripada is becoming more popular for companies in various industries. From food and beverage to consumer goods. It’s a tool that can be used to showcase latest products or services in a face to face environment with consumers. Furthermore companies recognise the importance of having brand ambassadors and reps on the ‘front line’ introducing the public to new innovations or delicious treats. This is done in the ‘field’; around shopping centers and in retail hot spots, expos and events, university campus’ and sport stadiums to name a few. Most campaign activities focus on customer facing roles including product demonstrations, direct selling and street training teams. However not all field marketing is consumer facing such as auditing and merchandising. Goals and outcomes of field marketing will differ from company to company. Some campaigns are designed to increase brand awareness or sales. While others may be to collect data and feedback about the product and its market. At Splatter we have all the tools necessary for the clients desired outcome to be achieved WHAT A FIELD MARKETING TEAM LOOKS LIKE. For successful field marketing campaigns companies might have dedicated teams within their business whose task it is to be creative and manage field marketing initiatives. However agencies are also on hand to support a campaign. By offering staff, management and infrastructure the client can focus on the more creative aspect of the campaign. A field marketing agency and marketing Team in Agripada tends to work in territories operating with reps within their own regions. Often overlooked by regional or national managers depending on the scale of the team. Although territory management is more important for wide scale national distributing business, smaller brands are recognising the importance of managing promotions on a more local scale using teams to promote, audit and sell in their regions.WHAT CAN FIELD MARKETING DO FOR YOUR BUSINESS?
1. PRODUCT DEMONSTRATIONS
As mentioned already, demo days are a popular tool of field marketing. These campaigns can stretch from as little as one week to 6 months however some are continuous and full time. For consumer goods this would mean having brand representatives in retail stores and around shopping centers, events or road shows. Finally The Brand Ambassadors are engaging with the consumer and showing them how the product or service works. This is important as it allows a potential buyer to get hands on experience and a feel of ownership of the product; most importantly the rep is also on hand to answers any questions the customer may have. Although a sell is great the main aim of a demo campaign is brand awareness. Food and beverage take a slightly differently approach. By handing out free samples and one off deals of their product around retail and events, consumers are getting a taste of the brands latest delicious treats and at the same time everyone loves free food! Sampling is a fun activation and is effective when bringing new products to the high street. Marketing Training Learn more about product demonstrations by checking out our in depth guide here.2. DIRECT SELLING
Much like product demonstrations these campaigns have brand reps or ambassadors at the center of them. The difference is it’s more about the selling of the product. Sales rep might have targets to adhere to. Finally these campaigns are super effective during peak times when the difference in a sale or not can be having a knowledgeable brand rep in store. Product Demonstrations Learn more about what direct selling is in our guide here.3. RETAIL AUDITS AND MERCHANDISING
Auditing takes the reps out off the front line and away from the consumer. Auditing teams are used by marketers to monitor traditional marketing strategies that they put in place across retail. Most of all audits ensure that the brand is represented as it should be on shelves and around retail hot spots. Examples are; checking POS is as it should be across the territories, promotions advertised and running and paid spaces such as gondolas are set up. The data collected from the teams can be useful for the marketers to negotiate better future deals. In addition it also allows for mistakes to be rectified there and then by the reps. Splatter offer a live system that can be monitored by the client in real team meaning that red flags in the field can be dealt with instantaneously .Store Audits and Merchandising To learn more about Audits and merchandising view our guide here.4. GUERRILLA MARKETING
When it comes to guerrilla marketing the gloves are off. They are usually low budget campaigns but with the right imagination and ideas they offer up some unprecedented results. Furthermore the term ‘Guerrilla Marketing’ itself is used to refer to campaigns that surprise consumers in locations and ways they might not usually expect. For that reason the experience remains with the consumer.5. PRODUCT SAMPLING
Product Sampling To learn more about sampling work and what that involves view our guide here. WHO DOES WHAT? FIELD MARKETING REP: These guys and girls are the cream of the crop, they are masters of everything. Sometimes they may be conducting training sessions on major proportion for a retailers whole selling team. Another role they find themselves in are in is in the field collecting data and conducted audits. Finally everything in between including sales, merchandising, and working at events. Their primary concern is to drive brand awareness across their region through face to face with consumer and staff on a retail level. Read about what being a field marketing rep is all about here. FIELD MARKETING MANAGER: The field manager’s role is to oversee the field reps; it is their duty to ensure the field marketing campaigns achieves the clients intended goal. As the manager of all the region, they hold the responsibility of ensuring that all reps are trained and directed towards the client’s goals. In addition the field marketing manager will work closely with the clients marketing executives to align the marketing objectives and goals with team in the field. Finally they will then report the findings and feedback from the team. Read more about what being a field marketing manager entails here. BRAND AMBASSADOR/BRAND REP As we know by now the BA role is one of the most crucial in field marketing. Ultimately they are usually supplied by the marketing agency and are tasked with promoting and representing the client’s brand. This can work well within a University by hiring a student to represent the brand around campus; this is perfect for low budget campaigns as sometimes all it takes is giving the BA some products to show off. Some larger scale business’ use celebrities to endorse their product and services by making them the face of their brand using social media to promote to their following. Learn about the various roles within the Field Marketing industry are by reading our guide here. You can also join our team by signing up here. DO YOU NEED FIELD MARKETING? Field marketing as you have seen is a useful tool to accompany other traditional marketing strategies. For example a company might pay a huge amount of money for prime advertising spot during a major sports event. However if this is the case it is important for the brand to follow up with demos in stores. If there is a brand rep placed in store the following few days after the advertising campaign the customer is more likely to come over and ask some questions about the product. Another reason you might need field marketing is to ensure your budget has been well spent. After investing into a large scale in-store promotion campaign you want to ensure that it is implemented to the standard agreed with the retailer. Data can be collected by auditing teams and analysed to see if the money had been well spent. Furthermore it also gives opportunity for future campaigns to implemented with higher efficiency and success.marketing Team in Agripada
Learning from Retail – Is it a Store or an Ad or an Exhibit?
In-shop Promotion, f to f Marketing Supplier, f to f Marketing Supplier, f to f Marketing Supplier in pune, In-shop Marketing, Kiosk Interactive marketing, Rural branding promotion, , campus promotion advertisement, RWA promotion advertisement, Market promotion advertisement, marketing Team in Agripada
]]>f to f Marketing Supplier in navi mumbai
Becoming Marketing Active: The Fulcrum Guide to Getting Started with Business Marketing – In the first part of our guide to becoming marketing active f to f Marketing Supplier in navi mumbai, we looked at some of the reasons that drive a business to start marketing (if you missed part one, check it out here). But once you’ve made the decision to embark on a marketing strategy for your business, what next? Where do you start and what steps should you take to ensure a smooth and successful process? As is so often the case in business (and life!), preparation is key. So before rushing into any kind of marketing, it’s important to take the time to plan, research and strategise for success. In order to create an effective marketing strategy, you need to develop a thorough understanding of your market, your competitors and your business itself. This means getting back to basics and equipping yourself with all the information you need to identify marketing activities that work for your brand. 1) Research your target market How much do you know about the target audience of your product or service? We’re not just talking about age, sex or occupation (though, of course, you need to know these too). To have the best chance of reaching your target market, you need to dig deeper and find out exactly what drives them towards purchase. What kind of triggers are they most likely to respond to? Which elements of the marketing mix have the most impact on them? How will your product or service benefit them? Understanding these aspects of your target audience will enable you to position and market your brand accordingly, so comprehensive market research is essential. It’s often easier (and more cost-effective) to outsource this type of research to a professional agency who will be better placed to obtain the information you need. 2) Analyse your competition In order to stay ahead of your competitors, you need to know who they are, what they’re doing and how they’re doing it. Once you’ve identified who your key business competitors are, look into the marketing methods they’re using and the way in which they have positioned their brand. What channels and platforms have they chosen to market their business? How are they promoting their brand and its products/services? Consider which elements are crucial to your own business and how you can position your brand in order to get ahead. 3) Define your objectives What do you want to achieve from your marketing activity? Whether it’s to increase your revenue, establish your business in a new market segment or improve brand awareness, setting clear, measurable marketing objectives is vital in understanding what steps need to be taken in order to achieve these goals. Make sure that each identified objective is specific (how much do you want to increase revenue by?), achievable (is it realistic?) and has a timeframe for accomplishment (are you aiming to achieve this goal in three months or a year?). You also need to make sure that your marketing objectives tie in with your overall business objectives. 4) Understand your business You may think you have a pretty good understanding of your business, but it’s surprising what insights can be achieved when you conduct a thorough SWOT analysis (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats). Be rigorous, be meticulous, and above all be brutally honest. Is a lack of staff training letting your business down? Are your prices too high to compete in today’s market? Arming yourself with this knowledge is invaluable in developing a marketing strategy that leverages your company’s strengths and addresses those areas which need to be improved. In the next instalment of the Fulcrum guide to becoming marketing active, we’ll be looking at the raft of marketing channels available and helping you to identify which ones are best for your business. If you have something to share on this topic, why not get in touch? Leave your comments below…
f to f Marketing Supplier in navi mumbai
Learning from Retail – Is it a Store or an Ad or an Exhibit?
In-shop Promotion, f to f Marketing Supplier, f to f Marketing Supplier, f to f Marketing Supplier in pune, In-shop Marketing, Kiosk Interactive marketing, Rural branding promotion, , campus promotion advertisement, RWA promotion advertisement, Market promotion advertisement, f to f Marketing Supplier in navi mumbai
]]>f to f Marketing Supplier in navi mumbai
Marketing and Sales companies f to f Marketing Supplier in navi mumbai with high quality, ethical, outsourced sales through transparent and effective business programs. We have a team of marketing and sales professionals and trainers who are committed to ensure effective delivery of the message from the client to a prospective customer. Our specialty is tailor-fitting our service to suit each individual client’s needs, ensuring compliance and delivering ethical sales every single time. We are focused on compliant and ethical selling that puts the needs of the customer first and we value transparency, integrity, diligence and hard work to ensure that our employees, clients and customers all get the best experience possible. We look for long term investments, in both our employees and our clients to ensure quality in our work, and in the opportunity for growth potential and stability for all parties involved.
Marketing
Door to Door Marketing
Face to Face Marketing
B 2 B Marketing
Field Marketing
Learning from Retail – Is it a Store or an Ad or an Exhibit?
f to f Marketing Supplier in navi mumbai
In-shop Promotion, f to f Marketing Supplier, In-shop Marketing, f to f Marketing Supplier in pune, Kiosk Interactive marketing, Rural branding promotion, , campus promotion advertisement, RWA promotion advertisement, Market promotion advertisement,
]]>f to f Marketing Supplier in pune
B2B Experiential Marketing – When does it work?
What is experiential marketing? On the rise in recent years, f to f Marketing Supplier in pune and experiential marketing is all about customer interaction with your brand. It offers a unique experience with products or services, allowing customers to get a feel for how they would use it in their lives. For years marketers have been trying to get customers to use and trial their products. In this way it’s not a new concept; there have however, certainly been some innovative spins on how it’s done. Let’s look at experiential marketing, how it can work for B2Bs and some of the ways it can help build your brand.Emotional + Experiential Branding = Experiential Marketing The two elements that underpin experiential marketing are emotional branding and experiential branding.
Emotional branding: is about building the relationship between your brand and customers. Promoting emotional benefits like brand trust, security and credibility as a result of engaging with your brand is crucial. Experiential branding: designs and creates interactions that are sensory in nature, which emotionally influences preferences, shaping brand perception, and influencing satisfaction and loyalty. An excellent experiential marketing campaign is able to fuse both elements seamlessly together. Experiential Marketing for B2Bs In recent years interest in B2B experiential marketing has grown and some of the initial hesitation surrounding it has been replaced with a working understanding, when to do it, and how it stimulates ROI. For B2Bs, experiential marketing is generally less obvious, with the focus often on services (for example) in place of B2C exciting product launches. Oftentimes the B2B budget is also stretched. However we are seeing marketers begin to recognise the potentials that the experience can offer consumers. “The success of brand experience within the B2C market has not gone unnoticed, and B2B marketers are waking up to the potential of brand experience. However, there is a long way to go before they catch up with their B2C counterparts.” – Graham Ede, Ion Group 3 Examples of B2B experiential marketing Location with B2Bs can be one of the major barriers, and while it may not be easy to do experiential marketing in quite the same way as B2C, there’s certainly room to employ some of the same principals. Creating sensory interactions that promote core feelings of trust, and awareness of your product or services is central to this. Fulcrum marketing in public spaces – Linked with experiential, some marketers use a form of Fulcrum marketing. They tend to hold this drive in places where there are high concentrations of business buyers. Branded promotional staff can offer business people the opportunity to enter in a promotion, or sign up to attend an event whilst promoting the benefits of the product. demonstrations & reward – as part of a targeted marketing strategy, those in the IT space can offer information via webinar or video, which can showcase some aspects of the technology solution. Some marketing and web-based tools such as offer a free trial period, together with online coaching via Skype. This allows the user to build confidence in using the tool, and to experience all of the benefits of the trial period. At the end of the trial period (7 days), the participant is given a report with feedback on how well they have used the tool. Then they are awarded a certificate. Surprises and games – Surprising customers by showing up where they least expect you, gifting them, or sending them a card is a way to provide an out of the box experience and drive brand awareness. Another option could be to exhibit at a partner’s event as IBM did. Their interactive stand came complete with a candy bar, and plasma screens which posted live tweets from event attendees. Digital technology such as apps and games are also opportunity areas, and while often costly, look set to become more widespread and affordable in future. Experiential marketing reflects the growing importance of emphasising emotions to build successful brands. Digital media offers expanding opportunities to offer such experiences. In the ever-competitive B2B marketplace, it’s no longer enough to rely on traditional modes for lead generation. B2B marketers need to consider the complete kit that is available to them including; social media, mobile, search, paid advertising, print, telemarketing and increasingly placing emotion at the heart of it all with an experiential approach.